Muy últil en muchos proyectos con ESP32, por su simplicidad respecto al BLE.
https://github.com/huecat/Conectar-ESP32-por-Wifi-Sin-Router
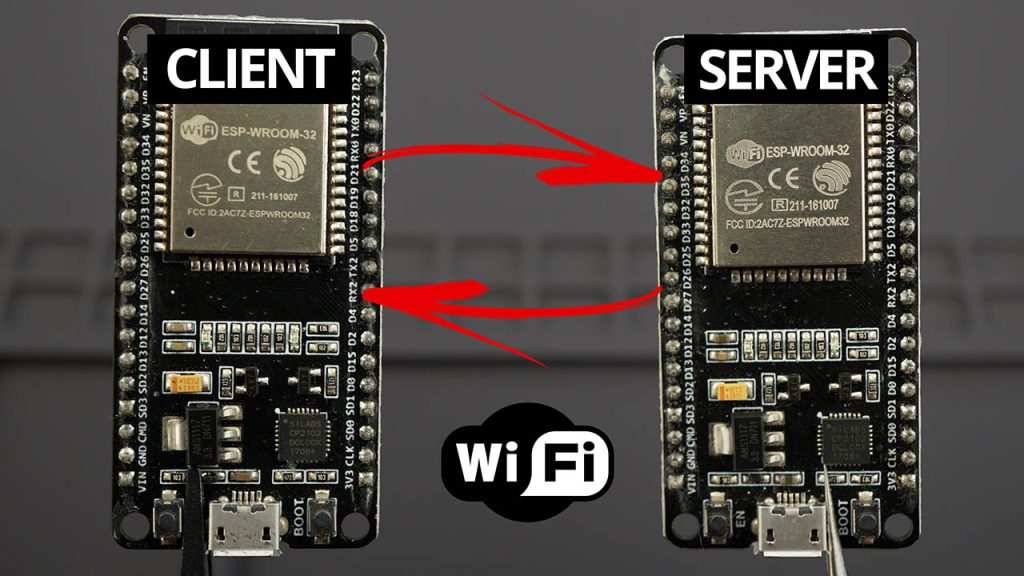
Servidor:
#include <WiFi.h>
const char* ssid = "Nombre_Red_Servidor";
const char* password = "Contraseña_Servidor";
WiFiServer server(80);
int buttonPin = 5;
int buttonState = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT_PULLUP);
// Configurar el ESP32 como un punto de acceso
WiFi.softAP(ssid, password);
IPAddress IP = WiFi.softAPIP();
Serial.print("AP IP address: ");
Serial.println(IP);
server.begin();
Serial.println("Server started");
}
void loop() {
WiFiClient client = server.available();
if (client) {
//Serial.println("New client connected");
while (client.connected()) {
// Leer el estado del botón
buttonState = 99;
//String response = String(buttonState) + "," + String(analogRead(A0)) + "," + String(random(100));
//client.println(response);
if (client.available()) {
String request = client.readStringUntil('\r');
Serial.print("Client says: ");
Serial.print(request);
Serial.print(", ");
int b = request.length();
//Serial.print("b=");
//Serial.println(b);
if (b > 2) {
int value1 = request.substring(0, request.indexOf(',')).toInt();
request = request.substring(request.indexOf(',') + 1);
int value2 = request.toInt();
Serial.print("Received values from client: ");
Serial.print(value1);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.println(value2);
}
}
//////// cada 3 segundos envia
static unsigned long a;
if (millis() > a + 5000) {
a = millis();
// Enviar dos variables simuladas al servidor
int value1 = 2; // Valor simulado 1
int value2 = 4; // Valor simulado 2
int value3 = 6; // Valor simulado 2
String response = String(value1) + "," + String(value2)+ "," + String(value3);
//String response = String(buttonState) + "," + String(analogRead(A0)) + "," + String(random(100));
Serial.print("Sending response: ");
Serial.println(response);
client.println(response);
client.stop();
}
}
//Serial.println("Client disconnected");
}
}
Cliente:
#include <WiFi.h>
const char* ssid = "Nombre_Red_Servidor"; // Reemplaza con el SSID de tu red
const char* password = "Contraseña_Servidor"; // Reemplaza con la contraseña de tu red
const char* serverIP = "192.168.4.1"; // Reemplaza con la dirección IP del servidor
const int serverPort = 80;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Conectándose a la red WiFi...");
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Conectado a la red WiFi. Dirección IP: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
}
void loop() {
// Simular dos valores enteros para enviar al servidor
int value1 = 1; // Valor simulado 1 (número aleatorio entre 0 y 9)
int value2 = 3; // Valor simulado 2 (número aleatorio entre 0 y 99)
// Construir la solicitud al servidor en el formato "value1,value2"
String request = String(value1) + "," + String(value2);
Serial.print("Enviando solicitud al servidor: ");
Serial.println(request);
// Establecer la conexión con el servidor
WiFiClient client;
if (client.connect(serverIP, serverPort)) {
// Enviar la solicitud al servidor
client.println(request);
// Esperar la respuesta del servidor
String response = client.readStringUntil('\r');
Serial.print("Respuesta del servidor: ");
Serial.println(response);
// Si necesitas utilizar los valores de la respuesta separados por comas, puedes hacerlo de la siguiente manera:
int serverValue1 = response.substring(0, response.indexOf(',')).toInt();
response = response.substring(response.indexOf(',') + 1);
int serverValue2 = response.substring(0, response.indexOf(',')).toInt();
//response = response.substring(response.indexOf(',') + 1);
//int serverValue3 = response.toInt();
Serial.print("Valores recibidos del servidor: ");
Serial.print(serverValue1);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(serverValue2);
//Serial.print(", ");
//Serial.println(serverValue3);
}
// Esperar 5 segundos antes de enviar una nueva solicitud
delay(5000);
}

Deja un comentario